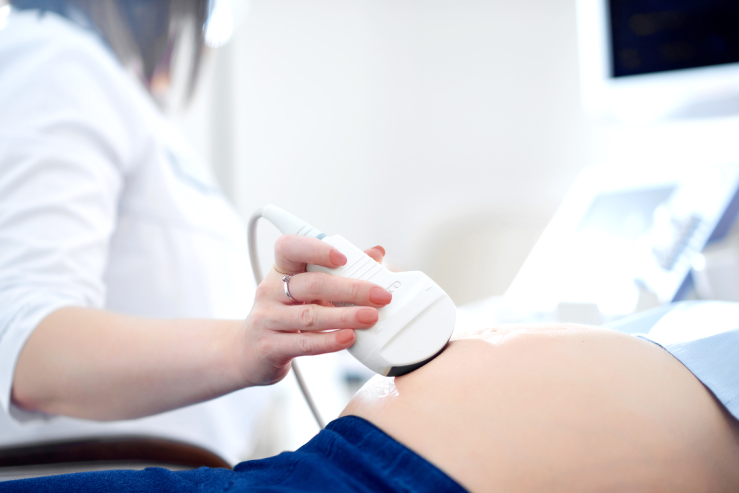
Ultrasonography, commonly known as ultrasound, is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the inside of the body. It helps in visualizing internal organs, tissues, and blood flow, enabling physicians to diagnose and monitor various health conditions.