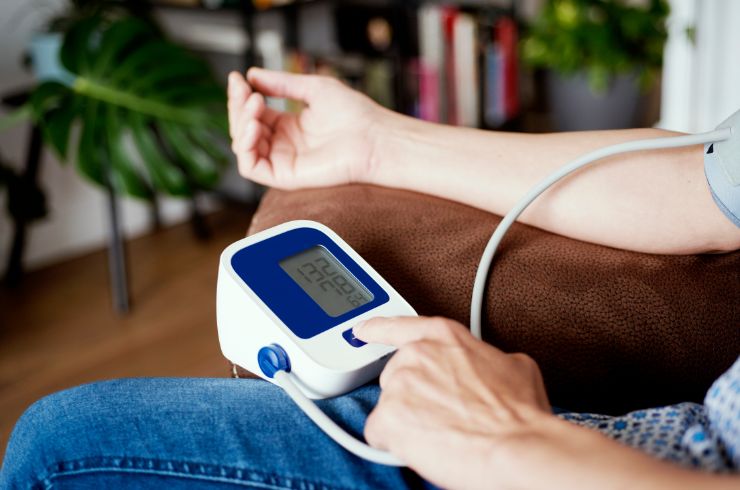
Ambulatory BP Monitoring is a diagnostic technique that measures your blood pressure at regular intervals over 24 hours while you go about your daily activities and sleep. This method provides a more accurate picture of your blood pressure compared to single measurements taken in a clinical setting, as it accounts for variations throughout the day and night.